Quick Answer (TL;DR)
Berberine and metformin share some mechanisms (AMPK activation), but they are fundamentally different:
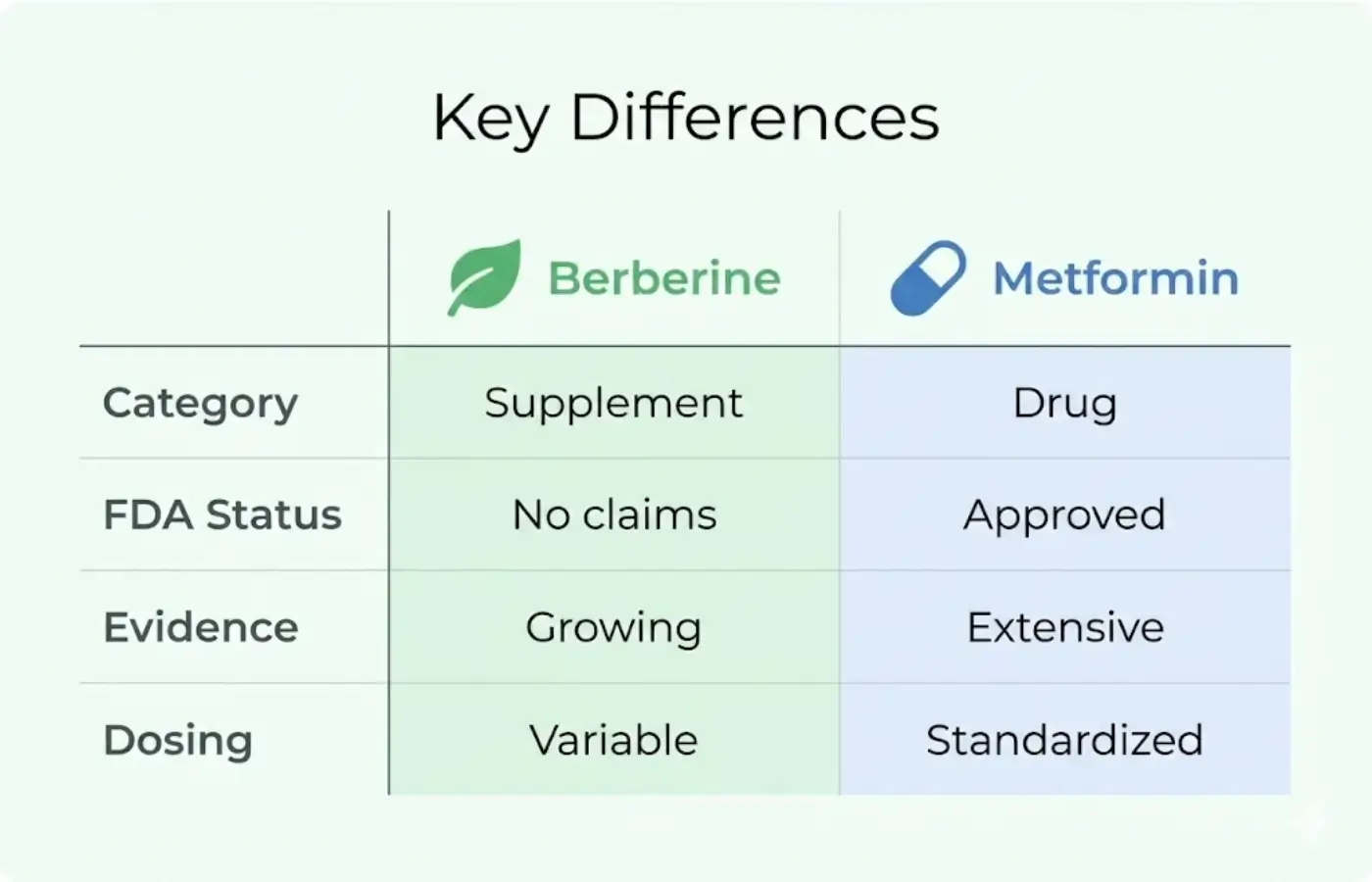
| Aspect | Metformin | Berberine |
|---|---|---|
| Category | Prescription drug | Dietary supplement |
| FDA status (US/PH) | Approved for T2D treatment | Supplement (no therapeutic claims) |
| Evidence quality | Extensive RCTs, decades of data | Growing, but less robust |
| Dosing consistency | Pharmaceutical-grade | Variable by brand |
⚠️ CRITICAL SAFETY NOTICE
- Do NOT stop or reduce metformin (or any diabetes medication) without your doctor’s approval.
- Berberine is a supplement, not an FDA-approved drug for diabetes treatment.
- This guide is educational—it does not diagnose, treat, or replace medical care.
- If you're pregnant/breastfeeding, avoid berberine (may cause uterine contractions).
🚨 Get urgent help if...
Severe hypoglycemia (confusion, shakiness, sweating, fainting), signs of DKA (fruity breath, nausea, difficulty breathing), or any sudden worsening → seek emergency care.
Affiliate disclosure: This article contains affiliate links.
For a full breakdown of a multi-ingredient formula that includes berberine, see: GlucosTrol Review Philippines (2026).